网站建设
深入剖析企业需求,致力于树立良好的企业品牌形象,完善企业对内外的传播需求。 积极协助企业找到发展战略核心,从战略的角度树立企业的品牌形象。
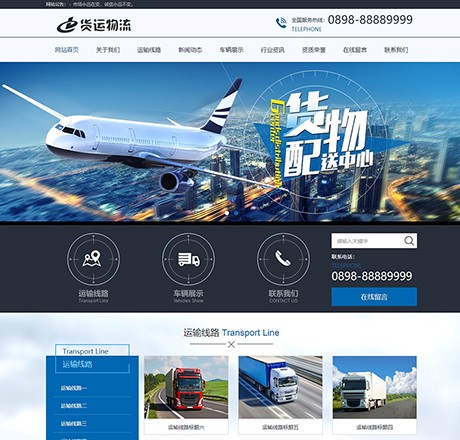
企业官方网站
通过企业文化及行业调研,独家订制属于企业的官方形象,十足的UI创意、尖端的制作技术及细节刻画提升,帮助企业在互联网上华丽转身。同时更为企业在线管理、信息发布打造最为便捷工具。
|
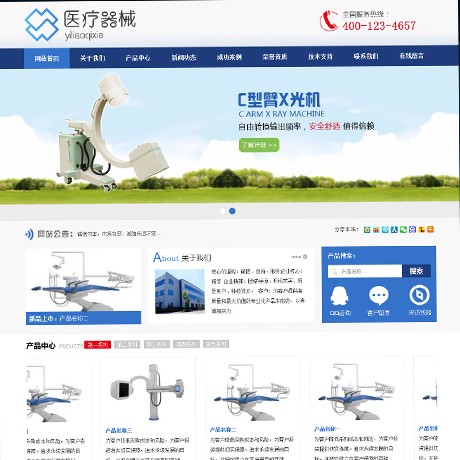
品牌网站
互联网时代,让品牌形象更富视觉冲击力,提升品牌影响力,同时使品牌资产得以进一步增值与溢价。将“业内尖端特效制作术”、“网络用户使用习惯”融为一体,打造赋予生命力的品牌网站。
|
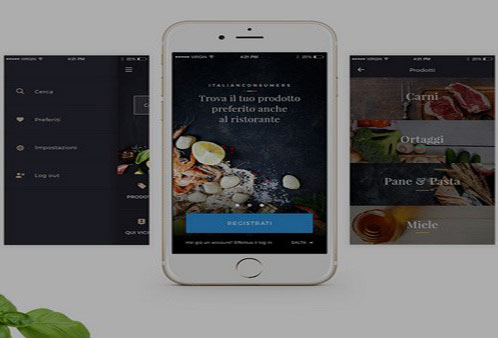
移动端网站
移动互联网营销是一个大的趋势, 但是怎么样去做恐怕还都一筹莫展。由PC端的网络营销的经验和常识来看,首要的是要做好移动端手机网站的优化工作。
|
模板展示
独一无二的原创设计,从PC、手机、移动终端,多网合一
关于我们
核心价值观:诚信、创新、服务 企业核心: 诚信 企业精神: 团结拼搏、开拓求实、满足用户、科技进步。 客户:为客户提供高质量和最大价值的专业化产品和服务,以真诚和实力赢得客户的理解、尊重和支持。 市场:为客户降低采购成本和风险,为客户投资提供切实保障。 发展:追求永续发展的目标,并把它建立在客户满意的基础上。 关于“为合作伙伴创造价值” 公司认为客户、供应商、公司股东、公司员工等一切和自身有合作关系的单位和个人都是自己的合作伙伴,并只有通过努力为合作伙伴创造价值,才能体现自身的价值并获得发展和成功。 关于“诚实、宽容、创新、服务” 公司认为诚信是一切合作的基础,宽容是解决问题的前提,创新是发展事业的利器,服务是创造价...
案例展示
我们擅长商业策略与用户体验的美妙结合。 用心做好每一个网站
新闻中心
我们擅长商业策略与用户体验的美妙结合。 用心做好每一个网站
|